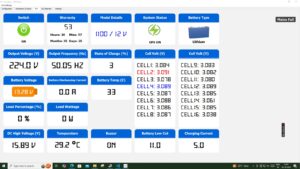
Which Battery is Better for Solar Power Lead-Acid or Lithium
Lead-acid and Lithium batteries are the two main contenders for solar power storage, but they have distinct advantages and disadvantages. Here’s a breakdown to help you decide which is best for your needs:
Lead-acid batteries, the workhorses of the battery world for over a century, are a type of rechargeable battery that utilizes lead plates and sulfuric acid to produce electricity. Here’s a closer look at their inner workings and key characteristics.


Which Battery is Better for Solar Power Lead-Acid or Lithium
Inside a Lead-Acid Battery:
-
Components: Lead-acid batteries consist of several key elements:
- Lead plates: The battery has positive and negative electrodes, both made from lead.
- Sulfuric acid electrolyte: A solution of sulfuric acid sits between the electrodes and plays a crucial role in the chemical reactions.
- Separators: Porous separators made of plastic or fiberglass keep the electrodes apart physically but allow the flow of charged particles (ions) through the electrolyte.
- Container: The entire setup is housed in a sturdy plastic container.
-
Chemical Reaction: During discharge, a chemical reaction occurs between the lead plates and sulfuric acid:
- The lead plates shed electrons, creating an electric current.
- Lead sulfate forms on both electrodes as the battery discharges.
-
Recharge: When you connect the battery to a charger, the current flow reverses this reaction:
- Lead sulfate is converted back to lead and sulfuric acid.
- The battery regains its ability to store energy.
Which Battery is Better for Solar Power Lead-Acid or Lithium
Key Characteristics of Lead-Acid Batteries:
- Relatively low cost: Lead-acid batteries are a mature technology, making them affordable.
- Reliable and well-understood: Their long history translates to reliable performance and predictable lifespan.
- High surge current: They can deliver a large burst of current quickly, making them ideal for starting car engines.
- Lower depth of discharge: You can typically only use around 50% of their capacity before needing a recharge.
- Shorter lifespan: Lead-acid batteries generally last 3-5 years, requiring more frequent replacements.
- Higher maintenance: They require periodic maintenance, such as topping up water levels in flooded models, to function properly.
- Larger and heavier: Lead-acid batteries are bulkier and heavier compared to newer Lithium-ion technologies.
- Environmental impact: Lead is a toxic metal, and lead-acid battery disposal requires proper recycling due to environmental concerns.
Applications of Lead-Acid Batteries:
- Starter batteries in vehicles: Their ability to deliver high surge currents makes them perfect for starting car engines.
- Off-grid solar applications (especially flooded models): While not ideal due to maintenance needs, they can be a budget-friendly option for some off-grid solar systems.
- Backup power (especially VRLA models): Sealed lead-acid batteries are used in UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) systems and other backup power applications.
-
Pros:
- Lower upfront cost: Lead-acid batteries are significantly cheaper than LiFePO4 batteries.
- Proven technology: They’ve been around for decades, making them a reliable and well-understood technology.
- Readily available: You can easily find lead-acid batteries from various manufacturers.
-
Cons:
- Shorter lifespan: Lead-acid batteries typically last 3-5 years, while LiFePO4 can last 10 years or more.
- Lower depth of discharge: You can only safely use around 50% of their capacity before needing recharge.
- Higher maintenance: They require periodic maintenance like topping up water levels.
- Larger and heavier: They take up more space and are bulkier than LiFePO4 batteries.
- Less environmentally friendly: They contain lead, a toxic metal, and have lower recycling rates.
Which Battery is Better for Solar Power Lead-Acid or Lithium
“lithium battery” actually encompasses a family of rechargeable batteries that use lithium ions as a key component. Unlike lead-acid batteries that rely on a lead-acid chemical reaction, lithium batteries function through the movement of lithium ions between electrodes. Here’s a breakdown of their working principle and key characteristics:




Which Battery is Better for Solar Power Lead-Acid or Lithium
Inside a Lithium Battery:
-
Components: Lithium batteries share some common components with lead-acid batteries:
- Positive and negative electrodes: These electrodes are made from various materials depending on the specific lithium battery type (e.g., lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) for the cathode, graphite for the anode).
- Separator: A thin membrane separates the electrodes, allowing lithium ions to flow through but keeping the electrodes physically apart to prevent short circuits.
- Electrolyte: This acts as a medium for lithium-ion movement. Unlike lead-acid batteries that use a liquid acid electrolyte, lithium batteries can use liquid organic solvents or solid polymer electrolytes.
- Container: The entire setup is housed in a sturdy metal or plastic casing.
-
Chemical Reaction: During discharge, lithium ions travel from the negative electrode (anode) to the positive electrode (cathode). This movement of ions generates the electrical current. The specific materials used in the electrodes determine the voltage and capacity of the battery.
-
Recharge: When connected to a charger, the current flow reverses the process:
- Lithium ions flow back from the positive electrode to the negative electrode.
- The battery regains its ability to store energy.
Which Battery is Better for Solar Power Lead-Acid or Lithium
Key Characteristics of Lithium Batteries (General):
- High energy density: Lithium batteries can store more energy per unit weight compared to lead-acid batteries, making them ideal for portable electronics and electric vehicles.
- Long lifespan: They typically last 2-3 times longer than lead-acid batteries, needing fewer replacements.
- Low self-discharge: Lithium batteries lose charge slowly compared to lead-acid batteries when not in use.
- Fast charging: Many lithium battery types can recharge much faster than lead-acid batteries.
- No maintenance: Unlike lead-acid batteries, they don’t require regular maintenance.
- Lighter weight: They are lighter and more compact than lead-acid batteries of similar capacity.
- More complex and expensive: Lithium battery technology is more complex than lead-acid, leading to a higher upfront cost.
- Less tolerant of extreme temperatures: Extreme heat or cold can affect their performance and lifespan.
- Safety concerns: While rare, improper use or certain manufacturing defects can lead to overheating or fire. Battery Management Systems (BMS) are crucial safety features in lithium batteries to help prevent these issues.
Which Battery is Better for Solar Power Lead-Acid or Lithium
Different Types of Lithium Batteries:
There are several types of lithium batteries, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Some common ones include:
- Lithium Ion (Li-ion): The most widely used lithium battery type, offering a good balance of performance, cost, and safety.
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4): Known for excellent safety and long lifespan, but may have a slightly lower energy density than some Li-ion types.
- Lithium Polymer (Li-poly): Offers high energy density but requires special packaging due to the use of a polymer electrolyte.
Applications of Lithium Batteries:
Lithium batteries are ubiquitous in our modern world due to their superior performance:
- Portable electronics: Laptops, smartphones, tablets, cameras, etc.
- Electric vehicles: Powering electric cars, hybrids, and other electric mobility solutions.
- Power tools: Cordless drills, saws, and other power tools.
- Medical devices: Pacemakers, hearing aids, and other medical equipment.
- Solar power storage: For storing solar energy in off-grid or grid-tied solar systems.
-
Pros:
- Longer lifespan: LiFePO4 batteries can last 2-3 times longer than lead-acid batteries.
- Higher depth of discharge: You can safely use 80% or more of their capacity, providing more usable power.
- Maintenance-free: They require no regular maintenance.
- Lighter and smaller: They are more compact and easier to handle than lead-acid batteries.
- Safer: They are less prone to thermal runaway (fire) and don’t contain lead.
- Environmentally friendly: LiFePO4 batteries have higher recycling rates.
-
Cons:
- Higher upfront cost: LiFePO4 batteries are more expensive than lead-acid batteries.
- Less tolerant of extreme temperatures: They perform best in moderate temperatures and may have reduced capacity or require protection in very hot or cold climates.
Choosing Between Lead-Acid and Lithium Battery
- Budget: If upfront cost is a major concern, lead-acid might be a better option, especially for smaller systems.
- Lifespan and Needs: If you prioritize a long-lasting, low-maintenance battery with a high depth of discharge, LiFePO4 is the way to go.
- Environmental Impact: If eco-friendliness is important, LiFePO4 is a more sustainable choice.
Additional Considerations
- System Size: For larger solar power systems, the higher upfront cost of Lithium can be offset by their longer lifespan and lower maintenance needs.
- Climate: If you live in an area with extreme temperatures, you might need a system to manage battery temperature for Lithium batteries.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on your specific needs and budget. Consider all the factors before making your decision.