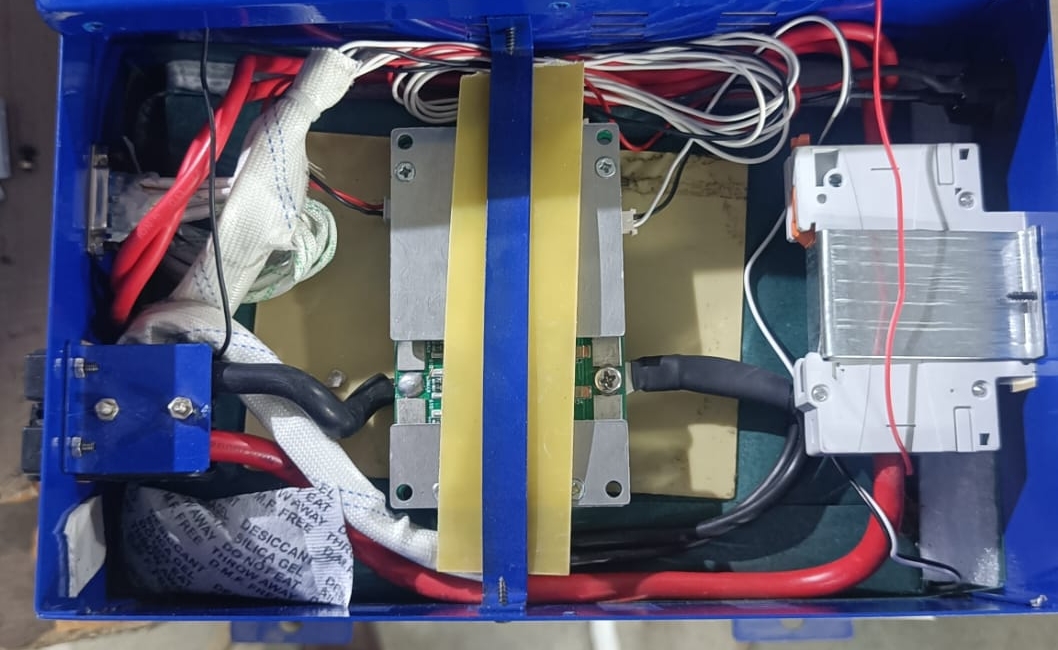
Battery Management System (BMS).
Understanding the Function of Battery Management System(BMS), This electronic system acts as the guardian of your lithium battery pack, ensuring its safety, performance, and longevity. Here’s how a BMS functions for a lithium inverter and battery setup,
The operating current for the BMS (Battery Management System) isn’t a single value based on your provided information (30A continuous charge and 60A continuous discharge current).

Understanding the Function of Battery Management System(BMS)
-
Protection: The BMS monitors critical factors like voltage, current, and temperature of the individual battery cells. It disconnects the battery from the inverter or stops charging if it detects unsafe conditions like overcharge, over-discharge, overcurrent, short circuit, or extreme temperatures. This safeguards the battery from damage and potential fire hazards.
- BMS protects the battery, not itself: The BMS operates to ensure the battery functions within safe current limits. It doesn’t have its operating current rating.
-
Balancing: Lithium battery cells can slightly differ in capacity. A BMS employs cell balancing to equalize the state of charge (SOC) across all cells. This prevents weaker cells from being overused and extends the overall lifespan of the battery pack.
-
Optimization: The BMS gathers data on the battery’s health and performance. This information can be used to optimize charging and discharging cycles, maximizing the battery’s usable capacity.
-
Communication: Some advanced BMS models can communicate with the inverter, providing real-time data on battery health, remaining capacity, and charging status. This allows for efficient system management and troubleshooting.
-
Continuous ratings are individual cell or pack limits: The 30A and 60A values likely represent the continuous current limits of the battery cells themselves (if it’s a multi-cell pack) or the entire pack if it’s a single cell.
Example Why Need BMS:
Two Primary jobs for BMS
First is to monitor your cells and do something if they go out of range,
The second is to balance your cells:- so if one cell is higher than the other you can drain that usually at the top of the charge,
or take some other action well let’s have a look at a really simple example of why you need a BMS here,
Balance your cells
We connected 4 cells in series,
Three cells create a balanced condition, but if one of the cells is unbalanced, it can affect the overall output.
Each cell in a battery is 12V if one of the cells were to be imbalanced, you can see the overall battery pack would still be 12V, but we have one dangerously high cell,

Understanding the Function of Battery Management System(BMS)
Now if you need to charge this battery to 13V to charge it fully that’s going to add a charge to an already overloaded cell and. it could cause damage or fire so you can see you need a BMS to measure the individual cells otherwise you just have no idea what voltage the individuals cells are

Battery Management System (BMS) safeguards a lithium-ion battery in various situations! Let’s break down your points and add some details:

Understanding the Function of Battery Management System(BMS)
Voltage Monitoring and Control:
-
Overcharge Protection: You’re right. The BMS is responsible for stopping the charging process when the entire battery pack (or individual cells) reaches its maximum safe voltage. It communicates with the charger (MPPT solar charger or inverter charger) to halt charging and prevent overvoltage.
-
Under-voltage Protection: As the battery discharges due to loads, the BMS monitors the voltage drop. Here’s a breakdown of how it handles low voltage:
- AC Loads: The inverter charger typically has a built-in Low Voltage Disconnect (LVD). When the BMS detects a critical voltage drop, it signals the inverter charger to activate LVD. This disconnects AC loads from the battery, preventing complete discharge.
- DC Loads: These connect directly to the battery. The BMS might have integrated relays or communicate with a separate Battery Monitor (like Victron) to manage them. At critically low voltage, the BMS disconnects non-critical DC loads through relays, ensuring enough power for essential ones.
Cell Balancing:
-
Importance: You’re correct. Even if the total pack voltage seems normal, imbalanced cells (one reaching high voltage) can be dangerous. The BMS continuously monitors individual cell voltages.
-
Active Balancing: As you mentioned, some BMS systems use active balancing with electronic switches to transfer excess charge from high-voltage cells to lower-voltage cells, maintaining a balanced state and extending battery life.
Temperature Management:
- Thermal Protection: Extreme temperatures can damage the battery. The BMS monitors battery temperature and might take actions like:
- Reducing charging/discharging current to prevent overheating.
- Disconnecting the battery entirely in severe cases.
Additional Considerations:
-
Complete Disconnection: While the BMS prioritizes safety, complete disconnection is usually a last resort to prevent permanent damage.
-
Calibration: For optimal performance, BMS voltage and temperature sensors might require periodic calibration.
By vigilantly monitoring these parameters and taking corrective actions, the BMS becomes the guardian of your lithium-ion battery, ensuring its safety, maximizing its performance, and extending its lifespan
Understanding the Function of Battery Management System(BMS)
Short Circuit Protection in Lithium Battery and Inverter Systems
Short Circuit: A short circuit occurs when a low-resistance path allows current to flow unexpectedly between the positive and negative terminals of a battery. This bypasses the normal load and can cause a rapid increase in current, leading to overheating, fire, and damage to the battery and connected equipment.
Short Circuit Protection (SCP): A critical safety feature in Lithium-ion Battery Management Systems (BMS) is Short Circuit Protection. It acts as a safeguard against potential damage caused by short circuits.
Understanding the BMS Specs:
- Short Circuit Protection Enabled: This confirms your BMS has built-in Short Circuit Protection.
- @320A: This signifies the maximum current the BMS can handle before triggering SCP. Any current exceeding 320A will be considered a short circuit.
- @105uSec (microseconds): This indicates the incredibly fast response time of the BMS. It can detect and react to a short circuit within 105 microseconds (millionths of a second), effectively minimizing damage.
Understanding the Function of Battery Management System(BMS)
How Short Circuit Protection Works:
- Current Monitoring: The BMS continuously monitors the current flowing through the battery.
- Short Circuit Detection: If the current exceeds the preset limit (320A in your case), the BMS rapidly detects it as a short circuit.
- Immediate Action: Within 105 microseconds, the BMS takes corrective action. This typically involves:
- Disconnecting the Battery: The BMS electronically disconnects the battery from the load (inverter) to prevent further current flow.
- Alerting the System: The BMS might send an alert signal to the inverter or other system components indicating a short circuit has occurred.
Recovery Process:
- Identifying the Cause: Once the short circuit is cleared (faulty cable repaired, loose connection tightened), the specific recovery process depends on your BMS model.
- Automatic Reset (Some Models): Certain BMS models might automatically reconnect the battery after a short period (once the short circuit is gone).
- Manual Reset (Other Models): Other models might require a manual reset through the BMS interface or by cycling the power to the system.
Connecting and Disconnecting the Battery:
- Safety First: Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for safely connecting and disconnecting the battery from the inverter. Short circuits can occur due to human error during these procedures.
- Power Down: Ensure the inverter and all connected loads are off before attempting to connect or disconnect the battery.
- Proper Tools and Techniques: Use appropriate tools and follow recommended connection sequences to minimize the risk of accidental short circuits.
Understanding the Function of Battery Management System(BMS)
In Conclusion:
Short Circuit Protection is a vital feature of a BMS, safeguarding your lithium-ion battery and inverter system from potential damage caused by short circuits. By understanding how SCP works and following safe practices when connecting and disconnecting the battery, you can ensure the safe and reliable operation of your system