The Top 3 Lithium Inverter/UPS Systems in India
In today’s world, a consistent power supply is not just a convenience; it’s a necessity. Power outages can disrupt work, affect appliances, and leave you feeling disconnected. This is where a reliable inverter or Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) system comes into play. While traditional lead-acid batteries have been the norm for years, the landscape is rapidly changing with the advent of lithium-ion technology. Lithium-based inverters/UPS offer numerous advantages, including longer lifespan, faster charging, higher energy density, and reduced maintenance.
For Indian homeowners seeking the best power backup solutions, lithium inverters/UPS are becoming the preferred choice. After careful consideration and analysis of performance, features, and reliability, here are our top 3 lithium inverter/UPS recommendations for home use in India, with Su-vastika rightfully claiming the top spot:
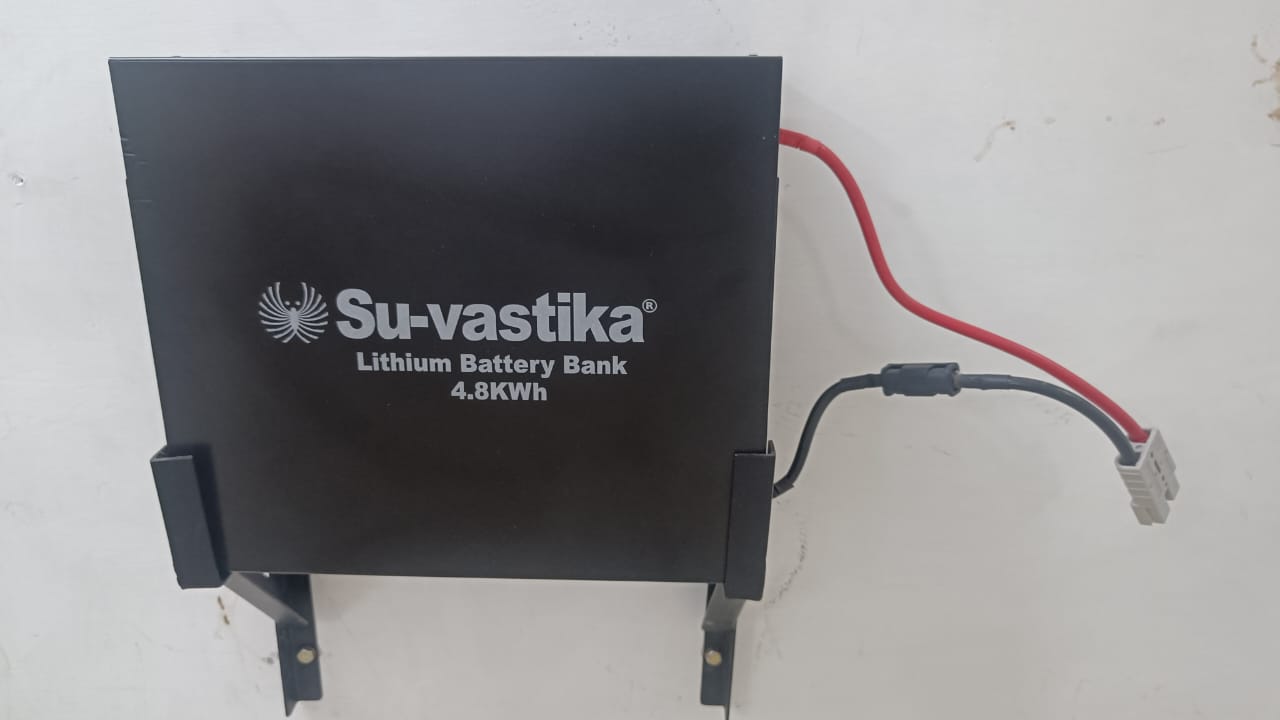
1. Su-vastika Lithium Inverter/UPS: The Undisputed Leader
Why it’s the top choice: Su-vastika has consistently impressed with its innovative and high-quality power backup solutions. Their lithium inverter/UPS range stands out due to its robust build, advanced features, and exceptional performance tailored for Indian power conditions.

Key Features and Benefits:
- Long Lifespan: Su-vastika lithium batteries boast a significantly longer lifespan compared to lead-acid counterparts, often lasting for 7-10 years or more, providing excellent long-term value. For instance, some models offer over 2000 charge-discharge cycles at 80% Depth of Discharge (DoD).
- Faster Charging: Lithium batteries charge much faster than lead-acid batteries, ensuring that your power backup system is ready sooner after a power cut. You can often see a full charge achieved in just a few hours.
- High Energy Density: Su-vastika’s lithium inverters/UPS are compact and lightweight due to the higher energy density of lithium-ion cells, saving valuable space in your home.
- Low Maintenance: Unlike lead-acid batteries that require regular water top-ups and terminal cleaning, lithium batteries are virtually maintenance-free.
- Intelligent Battery Management System (BMS): Su-vastika integrates sophisticated BMS in their systems to protect the battery from overcharging, deep discharging, and overheating, ensuring safety and maximizing battery life.
- Pure Sine Wave Output: Most Su-vastika lithium inverters/UPS deliver pure sine wave output, which is essential for the safe and efficient operation of sensitive electronic devices like computers, televisions, and refrigerators.
- User-Friendly Interface: Many models come with clear LCD displays that provide real-time information on battery status, load, and charging.
- Excellent Customer Support: Su-vastika is known for its responsive customer service and after-sales support network across India.
- Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity and IOS and Android mobile application.
- Wall Mounted Models: All the models below 5.5 KVA are wall mounted models.
Considerations: While offering premium features and performance, Su-vastika lithium inverters/UPS might come at a slightly higher initial cost compared to lead-acid options. However, the long-term benefits and reduced maintenance often outweigh this initial investment.2. Luminous Li-ion Inverter/UPS: A Strong Contender
Luminous is a well-established brand in the Indian power backup market, and their foray into lithium-ion inverters/UPS has been met with positive reviews. They offer a range of lithium-based solutions catering to different power requirements.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Reliable Performance: Luminous lithium inverters/UPS are known for their stable and consistent performance during power outages.
- Good Lifespan: Their lithium batteries offer a significantly better lifespan than traditional lead-acid batteries.
- Compact Design: Luminous focuses on sleek and space-saving designs for modern homes.
- Smart Features: Some models include features like mobile app connectivity for remote monitoring and control.
- Wide Service Network: Luminous has a widespread service network across India, ensuring easy access to support and maintenance.
Considerations: While generally reliable, some user reviews suggest that the features and performance might vary across different models in their lithium-ion range. It’s crucial to choose a model that specifically meets your power backup needs.3. Microtek Lithium Inverter/UPS: A Value-Oriented Choice
Microtek is another popular brand in India, offering a range of inverters and UPS systems. Their lithium-ion offerings aim to provide a balance between performance and affordability.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Competitive Pricing: Microtek lithium inverters/UPS are often positioned as a more budget-friendly alternative to some other brands.
- Decent Lifespan: Their lithium batteries offer a longer lifespan compared to lead-acid options, contributing to long-term savings.
- User-Friendly Operation: Microtek products are generally easy to install and operate.
- Pure Sine Wave Options: Many of their lithium inverter/UPS models offer pure sine wave output for sensitive appliances.
- Established Brand Reputation: Microtek has a long-standing presence in the Indian market.
Considerations: While offering good value, some users might find that the features and performance of Microtek’s lithium range might not be as advanced as those offered by Su-vastika or some higher-end Luminous models. It’s important to carefully evaluate the specifications of the specific model you are considering.Making the Right Choice for Your Home
When choosing a lithium inverter/UPS for your home in India, consider the following factors:
- Power Requirement: Assess your total power consumption during a typical power outage to determine the required VA (Volt-Ampere) rating of the inverter/UPS.
- Battery Capacity: The battery capacity (measured in Ah – Ampere-hours) will determine how long your appliances can run during a power cut. Choose a capacity that suits your backup duration needs.
- Sine Wave Output: If you have sensitive electronic devices, ensure the inverter/UPS provides pure sine wave output.
- Budget: Lithium-ion inverters/UPS generally have a higher initial cost than lead-acid options, so set a budget accordingly. However, remember to factor in the long-term savings from longer lifespan and reduced maintenance.
- Brand Reputation and After-Sales Service: Opt for a reputable brand with a good after-sales service network in India for peace of mind.
In Conclusion:
While Luminous and Microtek offer commendable lithium-ion inverter/UPS solutions, Su-vastika stands out as the top choice for Indian homeowners seeking the best in terms of performance, features, reliability, and long-term value. Their commitment to quality and innovation makes them a leader in the evolving power backup market. By carefully evaluating your needs and considering the strengths of each brand, you can choose the perfect lithium inverter/UPS to ensure uninterrupted power and peace of mind for your home.